AI-Assurance - AI-Agentic & Vibe Testing Revolution. Is this the end for coders / SDETs or a new role for future-proofing testers?
A seismic shift is reshaping software testing—and most testers don’t even see it coming. In the Valley, “Vibe Testing” and Agentic-AI systems are no longer marketing hype. At Microsoft, over 30% of production code is already generated and co-ordinated by autonomous AI agents. The gap between AI-augmented teams and traditional ones grows wider every day.
This isn’t just another workshop — it’s your career accelerator. In just a few hours, you’ll get hands-on with the tools redefining software engineering: rapidly generating and executing thousands of intelligent tests with Testers.AI, fixing complex issues in real time using Cursor.com, and mastering a new infinity testing loops that renders outdated DevOps and Agile practices obsolete.
You’ll leave equipped to:
– Slash augmented testing activities from weeks to minutes
– Gain real world practical skills your peers don’t yet know exist
– Take the lead in emerging roles like AI-Assurance and Agentic Testing
As AI transforms how software is built, tested, and shipped, a new category of expertise is emerging—those who can wrangle AI, validate its outputs, and assure safety at scale.
The most dangerous belief in tech today? Thinking there’s still time to catch up.
The AI testing revolution is already here. This workshop gives you the skills to secure your future!
Workshop agenda:
Module A – Vibe Testing
1. Introduction to Vibe Testing
– Definition of vibe testing is, distinguishing it from design engineering software techniques such as “vibe testing”
– Timeline and evolution (2020-2022)
– How Microsoft Test – the trending approach that Microsoft and other companies are already using in Silicon Valley
– Industry adoption (Microsoft claims 30% of production code is AI-generated)
– Current limitations, dark side and impact on skills gap
2. Tools and Environment Setup for Vibe Coding
– Hands on vibe coding:
*Testers.AI [MCP]
*Jonathon.ai [RARE]
*Cursor.com (for code generation) [Anthropic]
*LM Studio for running models offline without internet dependency [Mistral]
– Domain-specific language models (DSM) with industry knowledge
– Importance of offline processing for security and proprietary information protection and impact of the EU AI Act and AI Liability Laws.
3. Practical Implications and Demonstrations
– Hands on Vibe Coding using Cursor for generating code
– Hands on Vibe Testing using testers.ai to generate and execute test cases
– Running hundreds of tests automatically against websites or applications
– Finding accessibility, security, and performance issues
– Code generation with context-aware understanding of applications
– How Computer Use Agents (CUA) test applications beyond web (like desktop and embedded systems)
– Demonstration of bug finding and fixing source code with automated tools
4. Limitations and Future of Vibe Coding
– Discussion about how vibe coding might only be relevant for a few years
– Concerns about code quality when using AI-generated code
– The balance between using AI to generate code/tests and maintaining human oversight
– Concerns about developer skills degradation when relying too heavily on vibe coding
Module B – AI-Agentic Testing
1. Fundamentals of Agentic AI
– Definition of agentic systems (AI systems that can act autonomously)
– History of agentic AI (Dr Tariq Kings work from 1995 to present)
– Comparison with traditional RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
– How agents can work together like a hive of bees – each with limited capabilities but collectively powerful
2. Practical Applications of AI-Agentic Testing
– Testing of agentic AI platforms and multi-agents (generating and running tests)
– Fixing code and triaging bugs
– Automating tasks previously done by humans (process mining with MS Copilot + Studio)
3. Reasoning and Memory in Agentic AI
– Importance of reasoning engines in agentic systems
– Short-term vs. long-term memory for agents
– How agents can use vision and action models to navigate interfaces
– Retrieval Augmented Graph Modelling (RARE) for information access
– Digital Twin Definition Language (DTDLv2) Graph modelling for application understanding
– Business and industry context for informed decision making
4. Computer Use Agents (CUA)
– Explanation of what CUAs is and how they can interact with computer interfaces
– Demo of browser-based agents and how they use reasoning to navigate interfaces
– Explanation of how agents can learn to use applications they’ve never seen before
– Microsoft’s implementation of CUA MS AgentOS using MS Graph (QL)
5. Core Technologies Behind Agentic AI
– Vision models for interface recognition
– Action models for interface interaction
– Reasoning engines for decision making
– Short-term and long-term memory systems
6. Building Agentic Systems
– Microsoft’s Autogen framework
– Setting up agent workflows
– Agent-to-agent communication (A2A)
– Agent orchestration and management
7. Applications and Implementation
– Testing applications at scale
– Finding and fixing code issues
– Business process automation
– Industry-specific applications (healthcare, automotive, etc.)
8. Ethical Considerations and Future Trends
– Concerns about AI-workforce replacement (AIWR)
– Emerging role for Quality Engineers shifting to AI-Assurance
– Regulatory aspects (42001, AI Act, GDPR, etc.)
– The changing role of testers in an agentic AI multi-system agent ecosystems
– How humans can work alongside agentic systems (transcendence)
– Future directions in agentic A
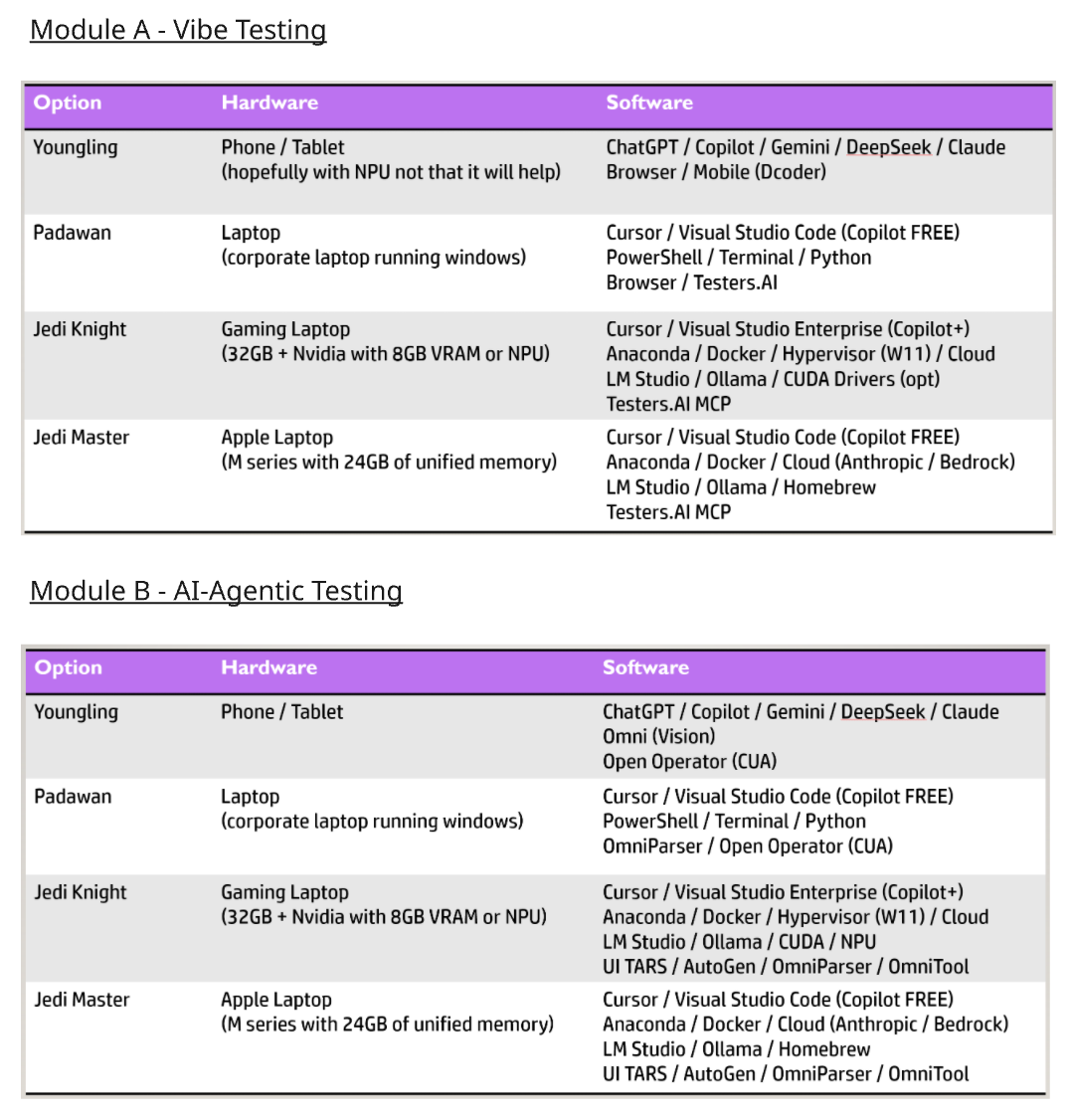
ATTENDEE HARDWARE & SOFTWARE REQUIEREMENTS:
We can't wait to see you all rocking the contest. Awesome prizes are waiting as well!
To take part, you have to have a valid AgileTD 2025 conference ticket (Online Pass or Onsite Ticket)!
Online attendees can join online only, Onsite attendees can join onsite.
Seats for both options are limited! First comes, first registered. We will inform all applicants - if they made it in or not - via email closer to the event. The sooner you apply, the better.
Apply to join Hackathon Get your AgileTD Ticket
